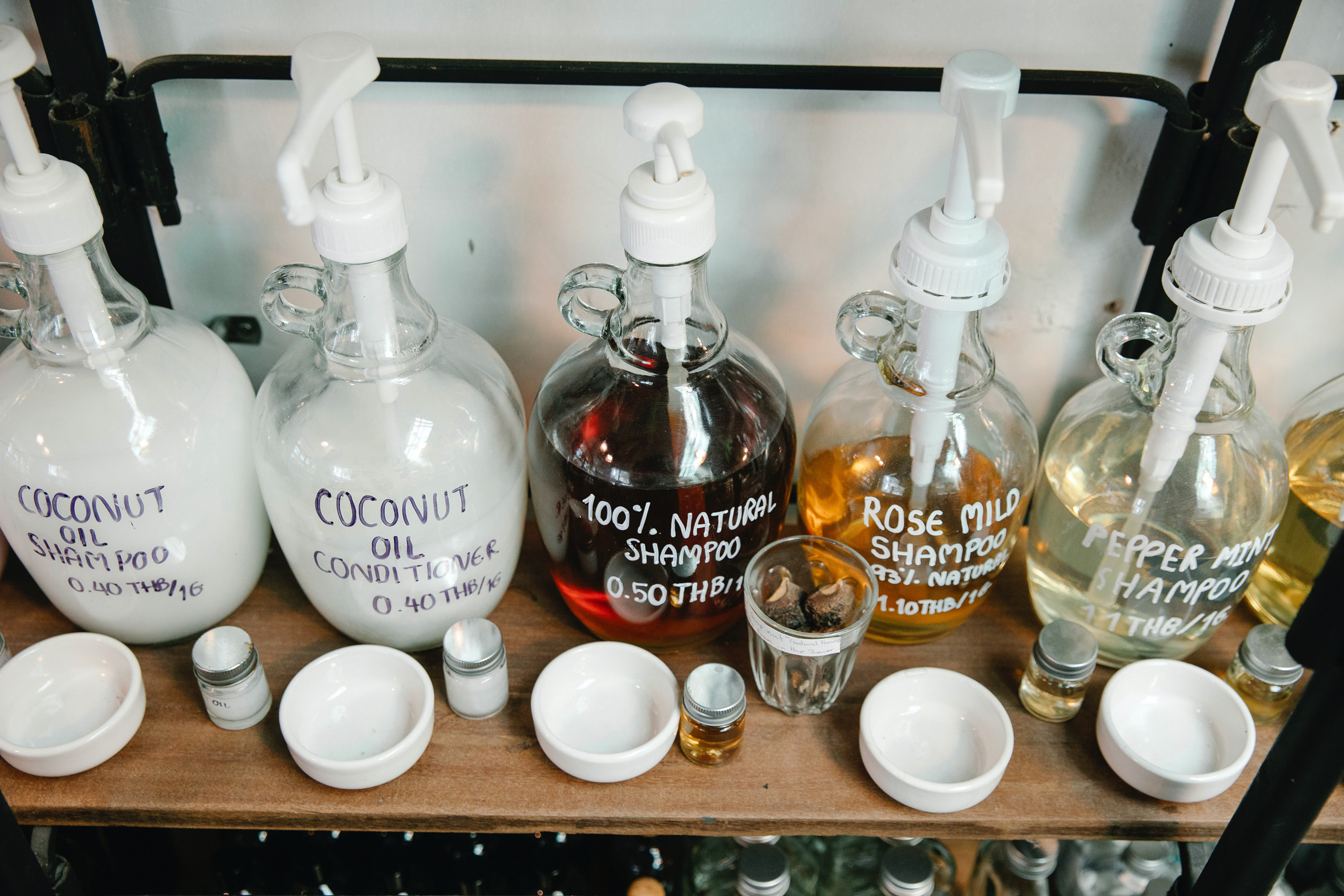
Shampoo: Raw Materials
To create a shampoo product, it is crucial to establish the specific features you intend to incorporate. These features encompass factors like the consistency, scent, and hue of the shampoo, as well as its cleaning efficiency, foaming ability, and overall texture. Typically, consumer feedback is utilised to determine the ideal combination of these characteristics for the product.
Below is a roster of the fundamental components that make up shampoo formulations.
Water
The primary component of shampoo is water, making up approximately 70 to 80% of the recipe. The inclusion of water assists in diluting the detergents, decreasing irritation and enhancing the dispersion of the formula. Furthermore, it is a cost-effective factor that minimises expenses. Additionally, you may find it interesting to examine battery pumps to better understand their involvement in the production of shampoos.
Detergents
A surfactant called detergent is the primary ingredient responsible for cleaning shampoos, making up 10 to 15% of the formula. These substances are typically derived from natural fatty acids that come from petroleum derivatives. Popular detergents utilised in shampoos are Ammonium Lauryl Sulfate, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, and Sodium Laureth Sulfate. Some natural shampoo manufacturers choose to use alternatives like Decyl Glucoside and Lauryl Glucoside instead.
Foam Boosters
Shampoo manufacturers often add surfactant types to enhance the foaming properties of their products, even though this does not necessarily affect the product’s performance. The common compounds used to boost foam and bubble size are alkanol amides and betaines. While most consumers prefer a creamy foam, the shampoo’s effectiveness is not impacted by this.
These components, Similar to the primary detergents, originate from fatty acids and possess qualities that allow them to dissolve in both water and oil. Common examples include Lauramide DEA or Cocamidopropyl Betaine, with a typical composition percentage ranging from 5-10%.
Thickeners
To some extent, secondary cleansing agents have the potential to increase the thickness of shampoo formulas. The addition of salt can also enhance the viscosity of shampoo. Additionally, the use of synthetic and cellulosic polymers such as Carbomer and Methylcellulose can increase the viscosity as well.
Conditioning Agents
In shampoo products, certain ingredients are used to counteract the negative impact of surfactants. These additional materials may include conditioning agents, quaternary agents, silicones, or polymers that leave a layer on the hair, resulting in enhanced softness, static reduction, and manageability. These types of shampoos are commonly referred to as 2-in-1 shampoos as they provide both cleaning and conditioning benefits in one easy step.
Common conditioning agents that are frequently used include certain polymers like Guar Hydroxypropyltrimonium Chloride and Polyquaternium-10, as well as silicones like Cyclomethicone and Dimethicone, and quaternary agents such as Quaternium 80. These agents are known to help improve the quality and texture of hair.
Preservatives
Cosmetic products containing water are prone to microbial and bacterial contamination, which is why preservatives are added to inhibit their growth. Methylparaben and DMDM Hydantoin are the two commonly used preservatives in shampoos. On the other hand, if you prefer natural alternatives, ingredients like Phenoxyethanol, Benzyl Alcohol, or Sodium Benzoate can be used as substitutes in a shampoo.
Other Ingredients
Shampoo may contain various compounds, beyond the main cleaning ingredients, such as dyes for hair colour, fragrances, pH adjusters, opacifiers, and chelating agents. Additionally, marketers may add “story ingredients” like herbal extracts, vitamins, and proteins for promotional purposes, which can impact the shampoo’s performance. Medicated shampoos, like anti-dandruff shampoo, have drug-active ingredients like zinc pyrithione.
The Manufacturing Process
The production process for shampoos involves the creation of sizable quantities of the product, which are subsequently packaged in various containers, such as bottles.
Compounding
Compounding refers to the mass production of cosmetics that involves combining various ingredients in a large stainless steel tank. Workers who are known as compounders are responsible for carrying out this process. Typically, the tank used for compounding is at least 3000 gallons in size.